In an increasingly digital world, the need for safeguarding our electronic devices has never been more critical. From common devices to crucial data housing, electromagnetic interference represents a significant threat to our technology. One effective solution to protect these devices is the Faraday cage, an innovation that remains a reliable solution. Whether you are concerned about EMPs, privacy issues, or want to make sure your gadgets remain functional in adverse conditions, understanding how to construct and use a Faraday cage can be an invaluable skill.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about Faraday cages, including how they function, the materials best suited for assembling, and key features to consider when purchasing or building one. With the right knowledge, you can adapt a Faraday cage to meet your specific needs, whether for personal electronics, emergency preparedness, or including for shielding your vehicle. Let’s explore the essential aspects of Faraday cages and discuss how to shield your devices from unwanted interference and vulnerabilities.
Comprehending Faraday Enclosures
A Faraday cage is a structure that blocks electrical fields and EM radiation from entering its within. It functions based on the principle of electromagnetic shielding, where a conductor responds to external electric fields by redistributing its charges, thus canceling out the field within. This indicates that any delicate electronics or information kept within a Faraday cage are safeguarded from external electromagnetic interference, making them more secure from potential dangers such as electromagnetic pulses, lightning hits, or illicit access to signals.
The efficacy of a Faraday enclosure is contingent upon several factors, including the material used, the construction of the cage, and its earthing. Materials like copper, aluminum, and steel are commonly used due to their conductivity. A mesh enclosure can deliver substantial protection, but solid materials tend to provide better protection against higher frequencies. When designing or picking a Faraday cage, it is important to take into account the intended uses and required level of safeguarding to ensure maximum effectiveness.
Faraday enclosures are not just restricted to commercial uses; they can be utilized in residential environments for multiple purposes, such as protecting personal electronics from EMPs and safeguarding sensitive data. With the growth of smart devices and the increasing issues around information security and electromagnetic exposure, understanding the characteristics and roles of Faraday cages has become more important than ever. By purchasing a quality Faraday cage, household and automotive users can greatly improve their safeguarding against unwanted electromagnetic threats.
Components and Dimensions Considerations
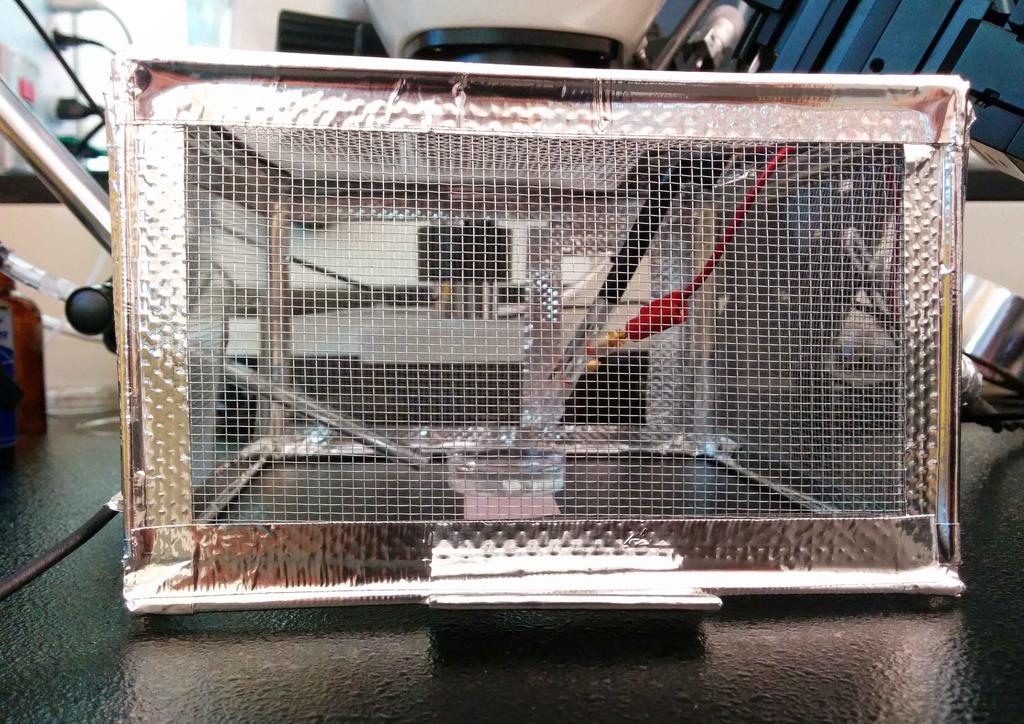
When choosing a Faraday cage, the materials used play a key role in its effectiveness. Alloys such as aluminium, coppers, and steels are the top choices due to their excellent conductive properties and capability to block electromagnetic waves. Aluminum is lightweight and immune to corrosion, making it easy to handle and maintain. Coppers offers superior conductivity and is incredibly effective for shielding against a wider range of frequencies. On the flip side, steel is durable and can provide a robust structural framework, though it may be more massive and more challenging to work with. Comprehending the properties of these metals will help you choose the right material for your Faraday cage to ensure maximum protection.
Dimensions is another important consideration when creating or buying a Faraday cage. The dimensions of your cage should be determined by the items you intend to safeguard. It's important to allow extra space for ventilation and additional additions, as well as to avoid crowded conditions that could diminish the protective effectiveness. For personal electronics, a small to medium-sized cage may suffice, while larger setups might be needed for multiple devices or bulkier appliances. Consideration of both inside and external dimensions will help ensure that your cage serves its purpose without losing accessibility.
In the end, the ideal material and dimensions for your Faraday cage will depend on your specific needs and usage scenarios. If portability is a priority, you might opt for a compact, light cage made of aluminium. Conversely, if you plan to store prized electronics for long periods, investing in a larger, more durable steel-made cage could be more beneficial. Balancing these two elements—substance and dimensions—will help you achieve a Faraday cage that not only shields against electromagnetic interference but also meets your practical requirements.
Evaluating and Upkeep
Once you have your Faraday cage set up, it is important to confirm its effectiveness in shielding electromagnetic signals. One standard method of testing is to place a active electronic device within the cage, such as a cell phone or a transmitter, and try to receive signals while the device is powered on. If the device does not receive any signals, this is a reliable indication that the cage is functioning properly. Alternatively, https://writeablog.net/faraday-cages36/are-faraday-cages-effective-against-emps-what-you-need-be-aware-of can utilize a radio frequency (RF) meter to assess the levels of electromagnetic radiation inside and externally the cage, confirming it adhere to the shielding standards needed for your devices.
Routine maintenance is important for ensuring continued protection. Over time, usage can affect the structural soundness of the Faraday cage. Examine for any physical damages like rust or dents, especially in metal cages. Make sure that door seals and connections are in good condition to maintain a steady barrier against electromagnetic interference. Wiping down https://dev-westudy.accedo.gr/members/faradayshields84/activity/2358839/ can also help, as dust and debris may affect its performance. If employing a mesh cage, check the mesh for any tears or gaps that could reduce shielding effectiveness.
For sustained operation, proper storage of the Faraday cage is crucial, especially for portable models. Store it in a cool place to prevent moisture damage, and if it is a DIY cage, keep it protected to avoid physical damage. It's wise to regularly test the cage after extended storage or changes in environment. This proactive approach will help ensure that your cage remains effective, giving you confidence that your electronics are secured when required.
